Virtual Machines : 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Ever wondered how one computer can run multiple operating systems at once? Welcome to the world of Virtual Machines (VMs)—a game-changing technology powering everything from cloud computing to software testing.
What Are Virtual Machines (VMs)?

At its core, a Virtual Machine (VM) is a software-based emulation of a physical computer. It runs an operating system and applications just like a physical machine, but it exists entirely in software. This allows multiple VMs to run on a single physical host, each isolated and functioning independently.
How Virtual Machines Work
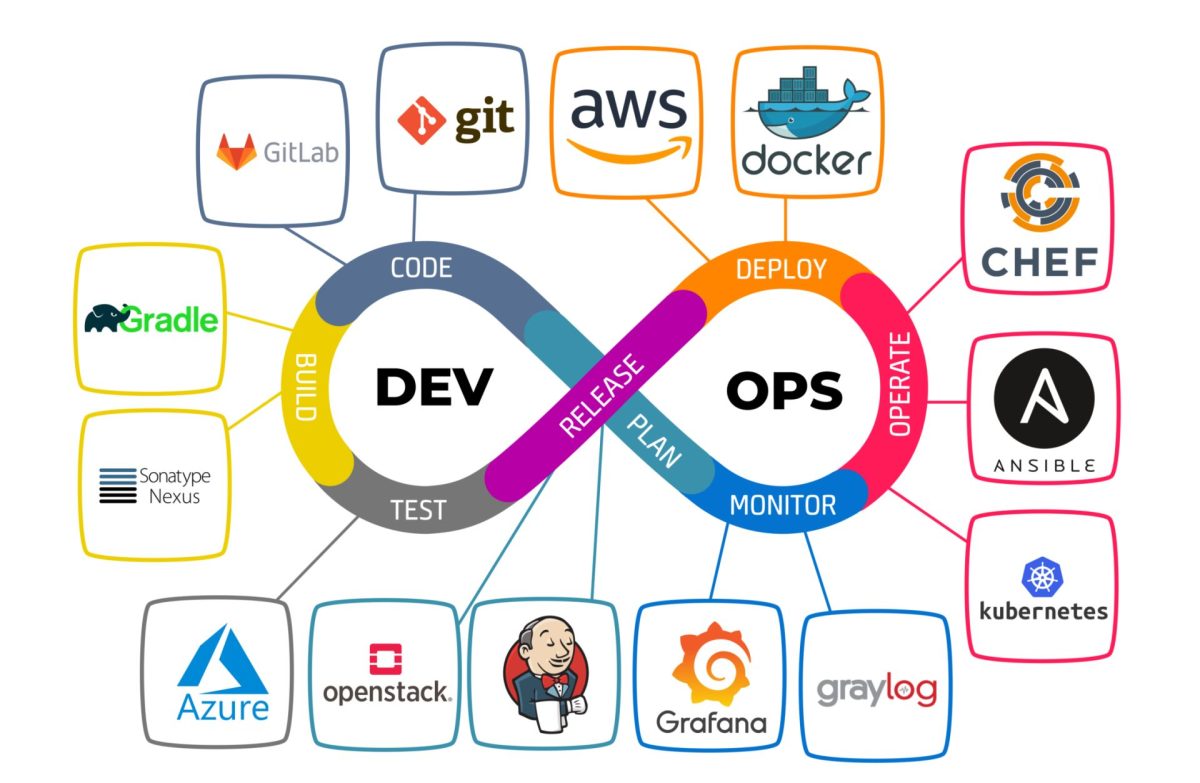
Virtual Machines operate through a layer of software called a hypervisor. The hypervisor sits between the hardware and the VMs, allocating resources like CPU, memory, storage, and networking to each virtual instance. Think of it as a traffic cop directing resources where they’re needed most.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- The hypervisor abstracts physical hardware resources.
- Each VM gets a virtualized set of hardware (vCPU, vRAM, virtual disk).
- VMs communicate with the host system through device drivers and virtual network interfaces.
There are two main types of hypervisors: Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted). Type 1 runs directly on the physical hardware—examples include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Xen. Type 2 runs on top of an existing operating system, like Oracle VM VirtualBox or VMware Workstation.
“Virtualization is not just a technology—it’s a strategy for efficiency, agility, and innovation.” — VMware
Key Components of a VM
A Virtual Machine isn’t just an OS in a box. It consists of several critical components that define its behavior and performance:
- Virtual CPU (vCPU): Emulates the processing power of a physical CPU.
- Virtual RAM: Allocated memory space from the host’s physical RAM.
- Virtual Disk: A file (like .vmdk, .vhd, or .qcow2) that acts as the VM’s hard drive.
- Virtual Network Interface Card (vNIC): Enables network connectivity for the VM.
- Guest Operating System: The OS installed inside the VM (e.g., Windows, Linux, BSD).
These components are defined in a configuration file that the hypervisor reads to instantiate the VM. When powered on, the VM boots just like a physical machine, loading its OS from the virtual disk.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Types of Virtual Machines (VMs)
Not all Virtual Machines are created equal. Depending on their purpose and architecture, VMs fall into different categories, each serving unique use cases in enterprise, development, and cloud environments.
System Virtual Machines
Also known as full virtualization VMs, system VMs provide a complete substitute for a physical machine. They allow multiple operating systems to run concurrently on the same hardware. This is the most common type used in data centers and cloud platforms.
For example, a single server running VMware ESXi can host dozens of Windows and Linux VMs, each running different applications. This maximizes hardware utilization and reduces the need for physical servers.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
System VMs rely heavily on hardware-assisted virtualization technologies like Intel VT-x and AMD-V, which improve performance by offloading virtualization tasks from software to the CPU.
Process Virtual Machines
Unlike system VMs, process VMs are designed to run a single application or process. They operate within a host OS and provide a platform-independent environment for executing programs.
A classic example is the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The JVM allows Java applications to run on any device that has a compatible JVM installed, regardless of the underlying OS or architecture. This is the foundation of Java’s “write once, run anywhere” philosophy.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Other examples include the .NET Common Language Runtime (CLR) and the Parrot VM for dynamic languages. While not as resource-intensive as system VMs, process VMs are crucial for cross-platform software development.
Benefits of Virtual Machines (VMs)
The rise of Virtual Machines (VMs) has revolutionized how organizations deploy, manage, and scale IT infrastructure. Their advantages span cost, flexibility, security, and efficiency.
Resource Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt VMs is the dramatic improvement in resource utilization. Physical servers often run at less than 15% capacity, wasting energy and space. VMs allow consolidation of workloads, enabling a single server to host multiple VMs.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
According to a VMware case study, organizations can achieve up to 80% server consolidation ratios using virtualization. This reduces hardware costs, power consumption, cooling needs, and physical footprint in data centers.
- Reduces the number of physical servers needed.
- Lowers energy and maintenance costs.
- Enables better ROI on hardware investments.
Isolation and Security
Each VM operates in isolation from others, even when running on the same host. This means that if one VM is compromised by malware or crashes due to a software bug, the others remain unaffected.
This isolation is a cornerstone of secure computing. For example, security researchers often use VMs to analyze malware in a sandboxed environment without risking their main system. Similarly, enterprises use VMs to separate critical applications from less secure ones.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Additionally, VMs can be configured with strict access controls, firewalls, and encryption, further enhancing their security posture.
“Virtual Machines provide a secure sandbox for testing and development, minimizing risk to production environments.” — Red Hat
Flexibility and Scalability
VMs offer unmatched flexibility in deployment and scaling. Need to spin up a new server for a development project? With VMs, it takes minutes—not days. Cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure rely heavily on VMs to deliver on-demand computing resources.
Scaling is equally simple. You can increase a VM’s CPU, RAM, or storage with a few clicks, often without downtime. This elasticity makes VMs ideal for handling variable workloads, such as e-commerce sites during holiday seasons.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Moreover, VMs can be easily cloned, migrated, or backed up, enabling rapid disaster recovery and high availability.
Virtual Machines (VMs) vs. Containers
As containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes gain popularity, a common question arises: Are VMs still relevant? The answer is yes—but understanding the differences is crucial for making the right architectural decisions.
Architecture Comparison
Virtual Machines include a full operating system, binaries, libraries, and the application, all running on top of a hypervisor. This provides strong isolation but comes with higher resource overhead.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
In contrast, containers share the host OS kernel and only include the application and its dependencies. They run on a container engine (like Docker) and are much lighter and faster to start.
- VMs: Heavyweight, full OS per instance, high isolation, slower startup.
- Containers: Lightweight, shared OS kernel, fast startup, lower isolation.
For example, a single server might run 10 VMs but hundreds of containers. However, containers are less secure by default because they share the kernel—if the kernel is compromised, all containers are at risk.
Use Case Scenarios
The choice between VMs and containers depends on the use case:
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Use VMs when: You need strong isolation, run different OS types, or require full OS functionality (e.g., legacy apps, databases).
- Use containers when: You want rapid deployment, microservices architecture, or high density (e.g., web apps, APIs).
In practice, many organizations use both. For instance, a cloud environment might run containers inside a VM for added security and flexibility.
Learn more about container vs. VM trade-offs from Docker’s official guide.
Popular Virtual Machine Platforms
A wide range of platforms support Virtual Machines (VMs), each with its own strengths, target audience, and ecosystem. Choosing the right one depends on your needs—whether you’re a developer, enterprise, or cloud provider.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
VMware vSphere/ESXi
VMware is a pioneer in enterprise virtualization. Its vSphere suite, powered by the ESXi hypervisor, is widely used in data centers for its robustness, scalability, and management tools like vCenter Server.
Key features include:
- Live migration (vMotion)
- High availability (HA)
- Distributed resource scheduling (DRS)
- Strong security and compliance features
VMware is ideal for large organizations but comes with a premium price tag. More info at VMware’s official site.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Microsoft Hyper-V
Built into Windows Server and available in Windows 10/11 Pro, Hyper-V is Microsoft’s native hypervisor. It integrates seamlessly with Active Directory, System Center, and Azure, making it a natural choice for Windows-centric environments.
Hyper-V supports:
- Generation 1 and 2 VMs
- Shielded VMs for enhanced security
- Live migration and failover clustering
- Direct integration with Azure for hybrid cloud scenarios
It’s a cost-effective option for organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Oracle VM VirtualBox
VirtualBox is a free, open-source hypervisor ideal for developers, testers, and students. It runs on Windows, macOS, Linux, and Solaris, supporting a wide range of guest operating systems.
Advantages include:
- No licensing costs
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Snapshot and cloning features
- Extensible via plugins and extensions
While not suited for enterprise production workloads, VirtualBox is perfect for learning, experimentation, and small-scale projects. Visit virtualbox.org for downloads and documentation.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Use Cases for Virtual Machines (VMs)
Virtual Machines (VMs) are not just a theoretical concept—they’re actively used across industries to solve real-world problems. From cloud computing to cybersecurity, their applications are vast and impactful.
Cloud Computing and Hosting
Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure rely on VMs to deliver Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). When you launch an EC2 instance on AWS, you’re essentially spinning up a VM in the cloud.
These VMs can be customized with different OS, CPU, memory, and storage configurations. Users pay only for what they use, enabling scalable, on-demand computing.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Cloud VMs also support auto-scaling, load balancing, and global distribution, making them ideal for modern web applications and enterprise workloads.
Software Development and Testing
Developers use VMs to create isolated environments for coding, testing, and debugging. Need to test an app on Windows 7, 10, and 11? Spin up three VMs—no need for multiple physical machines.
VMs also enable:
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Consistent development environments across teams
- Rapid setup and teardown of test environments
- Snapshot-based rollback to previous states
This accelerates development cycles and reduces “it works on my machine” issues.
Legacy Application Support
Many organizations still rely on legacy applications that only run on outdated operating systems like Windows XP or Windows Server 2003. Rather than maintaining aging hardware, companies virtualize these systems.
By running legacy apps in VMs, businesses can:
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Extend the life of critical software
- Reduce hardware maintenance costs
- Improve availability through VM snapshots and backups
- Migrate to modern infrastructure gradually
This approach is especially common in healthcare, finance, and manufacturing sectors.
Challenges and Limitations of Virtual Machines (VMs)
While Virtual Machines (VMs) offer numerous advantages, they are not without drawbacks. Understanding these limitations helps organizations make informed decisions and optimize their virtualization strategies.
Performance Overhead
Because VMs emulate hardware and run full operating systems, they consume more resources than bare-metal systems. The hypervisor itself uses CPU cycles and memory, and each guest OS has its own overhead.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
This can lead to:
- Reduced performance for I/O-intensive applications
- Higher latency compared to physical machines
- Resource contention when too many VMs share a host
To mitigate this, administrators use techniques like resource pooling, CPU pinning, and SSD storage. However, performance-critical applications (e.g., high-frequency trading) may still require physical servers.
Complexity in Management
Managing a large fleet of VMs can become complex. Issues include:
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- VM sprawl—uncontrolled proliferation of VMs leading to wasted resources
- Difficulty in tracking configurations and dependencies
- Backup and patch management across multiple OS instances
Tools like VMware vCenter, Microsoft System Center, and open-source solutions like Proxmox help manage this complexity, but they require skilled personnel and proper governance policies.
Security Risks
While VMs provide isolation, they are not immune to security threats. Potential risks include:
- Hypervisor vulnerabilities—if the hypervisor is compromised, all VMs on the host are at risk
- VM escape attacks—rare but dangerous exploits that allow attackers to break out of a VM into the host
- Snapshot and backup exposure—unencrypted VM images can leak sensitive data
To counter these, organizations implement defense-in-depth strategies: regular patching, network segmentation, encryption, and intrusion detection systems.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Future of Virtual Machines (VMs)
With the rise of containers, serverless computing, and edge computing, some have questioned the long-term relevance of Virtual Machines (VMs). However, VMs are evolving—not disappearing.
Hybrid Approaches: VMs and Containers
The future lies in convergence. Many modern platforms now run containers inside VMs, combining the best of both worlds: the security and isolation of VMs with the agility of containers.
For example, AWS Firecracker powers Lambda and Fargate by using lightweight VMs (microVMs) to run containers securely. These microVMs boot in milliseconds and have minimal overhead, blurring the line between VMs and containers.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Similarly, Google’s gVisor and Microsoft’s Drawbridge project explore hybrid models that enhance container security using VM-like isolation.
Edge and IoT Virtualization
As computing moves to the edge, VMs are being adapted for resource-constrained environments. Lightweight hypervisors like KVM and Xen are being optimized for IoT gateways and edge servers.
VMs enable:
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Running multiple applications on a single edge device
- Isolating safety-critical systems (e.g., in autonomous vehicles)
- Secure remote updates and monitoring
This trend will grow as 5G and AI drive demand for distributed, intelligent computing.
AI-Driven VM Management
Artificial intelligence is transforming VM management. AI-powered tools can predict resource needs, automate scaling, detect anomalies, and optimize performance in real time.
For instance, VMware’s Aria Operations uses machine learning to analyze VM workloads and recommend resource adjustments. This reduces manual intervention and improves efficiency.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
As AI matures, we’ll see self-healing, self-optimizing virtual environments that adapt dynamically to changing conditions.
What are Virtual Machines (VMs)?
Virtual Machines (VMs) are software emulations of physical computers that run operating systems and applications in isolation. They are managed by a hypervisor and can run multiple instances on a single physical host.
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
How do VMs differ from containers?
VMs include a full OS and run on a hypervisor, offering strong isolation but higher resource use. Containers share the host OS kernel, are lightweight, and start faster, but offer less isolation.
Are Virtual Machines secure?
Virtual Machines (VMs) – Virtual Machines (VMs) menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Yes, VMs are generally secure due to isolation between instances. However, risks like hypervisor vulnerabilities and VM escape attacks exist. Proper configuration, patching, and encryption are essential for security.
Can I run VMs on my personal computer?
Absolutely. Tools like Oracle VM VirtualBox and VMware Workstation allow you to run VMs on Windows, macOS, and Linux for testing, learning, or development.
What is the future of Virtual Machines?
VMs are evolving with microVMs, edge computing, and AI-driven management. They remain vital in hybrid cloud, security, and legacy support, often working alongside containers for optimal performance and isolation.
Virtual Machines (VMs) have transformed the IT landscape, offering unmatched flexibility, efficiency, and security. From powering the cloud to enabling legacy system modernization, their impact is undeniable. While challenges like performance overhead and management complexity exist, ongoing innovations ensure VMs remain a cornerstone of modern computing. Whether you’re a developer, IT professional, or business leader, understanding and leveraging VMs is key to staying competitive in today’s digital world.
Further Reading: