IoT Hub: 7 Powerful Insights You Must Know in 2024
Welcome to the world of connected everything! The IoT Hub is no longer just a tech buzzword—it’s the beating heart of smart homes, industrial automation, and next-gen cities. In this deep dive, we’ll explore how IoT Hubs work, why they matter, and what makes them indispensable in today’s digital ecosystem.
What Is an IoT Hub and Why It Matters

The term IoT Hub refers to a central communication platform that connects, manages, and secures Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Think of it as the central nervous system of a smart environment—whether it’s your home, factory floor, or city infrastructure. Without an IoT Hub, managing hundreds or thousands of devices would be chaotic and inefficient.
The Core Function of an IoT Hub
An IoT Hub acts as a bridge between IoT devices and the cloud. It collects data from sensors, sends commands back to devices, and ensures secure, real-time communication. This is critical in environments where latency, reliability, and scalability are non-negotiable.
- Aggregates data from multiple devices
- Enables bidirectional communication
- Supports device authentication and access control
“An IoT Hub isn’t just a connector—it’s a command center for intelligent automation.” — Microsoft Azure IoT Team
IoT Hub vs. Traditional Networking Devices
Unlike routers or switches, an IoT Hub is purpose-built for IoT ecosystems. While traditional networking hardware focuses on data transmission, an IoT Hub adds layers of intelligence, security, and device lifecycle management.
- Manages device identity and state
- Handles massive scale with low latency
- Integrates with analytics and AI platforms
For example, Azure IoT Hub supports millions of devices with built-in telemetry and command routing, making it ideal for enterprise deployments.
How IoT Hub Powers Smart Homes
One of the most visible applications of IoT Hub technology is in smart homes. From lighting and thermostats to security systems and voice assistants, an IoT Hub ensures all devices work in harmony.
Centralized Control and Automation
With an IoT Hub, homeowners can create automation rules—like turning off lights when no one is in a room or adjusting the thermostat based on weather forecasts. The hub processes triggers from sensors and executes actions across multiple devices.
- Enables scene-based automation (e.g., “Good Morning” mode)
- Reduces manual intervention through scheduling
- Supports integration with voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant
Security and Privacy in Home IoT Hubs
Security is a major concern in smart homes. A robust IoT Hub includes encryption, firmware updates, and access controls to prevent unauthorized access. For instance, hubs like Samsung SmartThings use end-to-end encryption and regular security patches to protect user data.
- Implements device authentication via certificates
- Monitors for suspicious device behavior
- Allows granular user permissions
Learn more about smart home security at Consumer Reports.
IoT Hub in Industrial Automation (IIoT)
In industrial settings, the IoT Hub becomes the backbone of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). It connects machinery, sensors, and control systems to enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and process optimization.
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
By collecting vibration, temperature, and pressure data from machines, an IoT Hub can detect anomalies before they lead to failure. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs significantly.
- Processes sensor data in real time
- Triggers alerts when thresholds are exceeded
- Integrates with AI models for failure prediction
Companies like Siemens and GE use IoT Hubs to monitor turbines and manufacturing lines, improving efficiency by up to 30%.
Scalability and Reliability in Harsh Environments
Industrial IoT Hubs are designed to operate in extreme conditions—high temperatures, electromagnetic interference, and remote locations. They often support edge computing to reduce reliance on cloud connectivity.
- Supports offline operation and local processing
- Uses ruggedized hardware for durability
- Ensures data integrity through redundant communication paths
Explore industrial solutions at Siemens Industrial IoT.
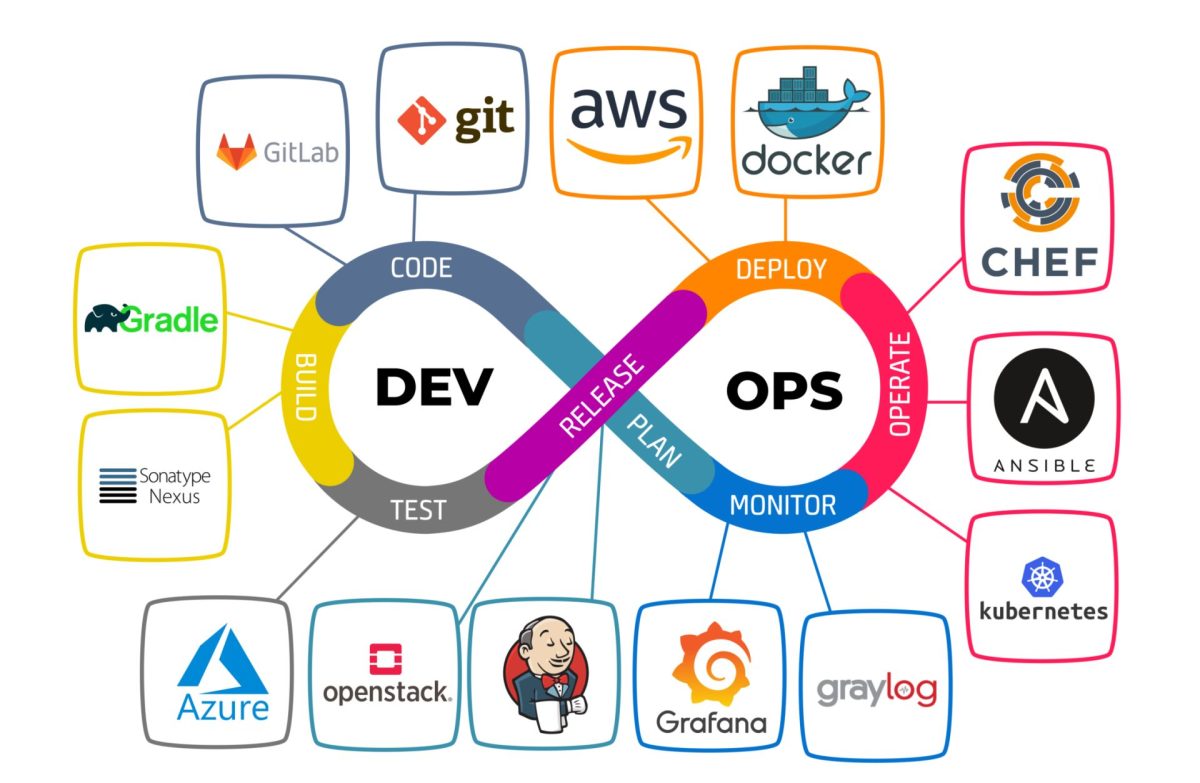
Top IoT Hub Platforms in 2024
Several platforms dominate the IoT Hub landscape, each offering unique features for different use cases. Let’s examine the most influential ones shaping the industry.
Microsoft Azure IoT Hub
Azure IoT Hub is one of the most comprehensive cloud-based IoT platforms. It supports device-to-cloud and cloud-to-device messaging, device twins, and robust security features.
- Supports MQTT, AMQP, and HTTPS protocols
- Offers device provisioning at scale
- Integrates seamlessly with Azure Machine Learning
Azure is widely used in healthcare, logistics, and smart city projects. Visit Azure IoT Hub for documentation and trials.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT Core
AWS IoT Core allows connected devices to securely interact with cloud applications and other devices. It’s highly scalable and integrates with AWS Lambda, S3, and Kinesis for data processing.
- Enables rule-based message routing
- Supports device shadows for state synchronization
- Provides fine-grained access control via IAM
AWS is a top choice for startups and enterprises needing flexible, pay-as-you-go IoT solutions. Learn more at AWS IoT Core.
Google Cloud IoT Core (Legacy & Alternatives)
While Google Cloud IoT Core was discontinued in 2023, its legacy lives on through Vertex AI and Cloud IoT Edge. Google now emphasizes AI-driven analytics and edge computing for IoT workloads.
- Leverages TensorFlow Lite for on-device ML
- Integrates with BigQuery for data analysis
- Focuses on sustainability and energy efficiency
Developers are encouraged to migrate to Vertex AI for next-gen IoT intelligence.
Security Challenges in IoT Hub Ecosystems
As IoT Hubs become more central to operations, they also become prime targets for cyberattacks. Ensuring end-to-end security is critical to maintaining trust and functionality.
Common Vulnerabilities in IoT Hubs
Many IoT Hubs suffer from weak default passwords, unencrypted communications, and outdated firmware. These flaws can be exploited to gain access to entire networks.
- Default credentials left unchanged
- Lack of secure boot mechanisms
- Insufficient over-the-air (OTA) update support
A 2023 report by Palo Alto Networks found that 98% of IoT traffic is unencrypted, exposing sensitive data.
Best Practices for Securing Your IoT Hub
Organizations must adopt a zero-trust approach to IoT security. This includes continuous monitoring, device authentication, and encryption at every layer.
- Use certificate-based authentication
- Implement network segmentation
- Regularly audit device access logs
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework provides guidelines for securing IoT deployments.
The Role of Edge Computing in IoT Hub Architecture
Edge computing is transforming how IoT Hubs process data. Instead of sending all data to the cloud, edge-enabled hubs perform local analysis, reducing latency and bandwidth usage.
Reducing Latency with Local Processing
In time-sensitive applications like autonomous vehicles or robotic surgery, even a millisecond delay can be critical. Edge computing allows IoT Hubs to make instant decisions without cloud round-trips.
- Processes data within milliseconds
- Supports real-time feedback loops
- Improves reliability in low-connectivity areas
Bandwidth Optimization and Cost Savings
By filtering and compressing data at the edge, IoT Hubs reduce the volume of information sent to the cloud. This lowers data transfer costs and minimizes network congestion.
- Only transmits relevant or aggregated data
- Reduces cloud storage requirements
- Extends battery life for remote sensors
Platforms like Digi Remote Manager offer edge-to-cloud IoT Hub solutions.
Future Trends Shaping the IoT Hub Landscape
The IoT Hub is evolving rapidly, driven by AI, 5G, and sustainability demands. Understanding these trends helps businesses stay ahead of the curve.
AI-Powered IoT Hubs
Future IoT Hubs will embed artificial intelligence to detect patterns, predict failures, and automate responses without human input. This shift from reactive to proactive systems will redefine efficiency.
- Uses machine learning for anomaly detection
- Enables self-healing networks
- Optimizes energy use in smart buildings
5G and Ultra-Low Latency Networks
With 5G rollout accelerating, IoT Hubs will benefit from faster speeds and lower latency. This enables massive IoT deployments in smart cities, drones, and augmented reality.
- Supports up to 1 million devices per square kilometer
- Enables real-time video analytics from drones
- Facilitates vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication
Learn about 5G’s impact at Ericsson 5G.
Sustainability and Green IoT Hubs
As environmental concerns grow, IoT Hubs are being designed for energy efficiency and recyclability. Solar-powered hubs and low-energy protocols like LoRaWAN are gaining traction.
- Reduces carbon footprint of IoT networks
- Supports smart grid and water conservation
- Promotes circular economy in hardware design
Choosing the Right IoT Hub for Your Needs
Selecting the right IoT Hub depends on your specific requirements—scale, security, budget, and integration needs. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision.
Key Evaluation Criteria
Before committing to a platform, assess the following factors:
- Scalability: Can it handle your projected device count?
- Security: Does it support end-to-end encryption and device authentication?
- Integration: Does it work with your existing software stack?
- Cost: Are pricing models transparent and predictable?
- Support: Is there reliable technical documentation and customer service?
Use Case-Based Recommendations
Different scenarios call for different solutions:
- Smart Home: Consider hubs like Hubitat Elevation or Home Assistant for local control and privacy.
- Industrial Monitoring: Azure IoT Hub or AWS IoT Core offer enterprise-grade reliability.
- Remote Sensing: LoRaWAN gateways with edge processing are ideal for agriculture or environmental monitoring.
IoT Hub Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The convergence of IoT Hubs with AI is unlocking unprecedented capabilities. From predictive analytics to autonomous decision-making, this integration is transforming industries.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Maintenance
By feeding IoT Hub data into machine learning models, organizations can predict equipment failures before they occur. This is especially valuable in manufacturing, energy, and transportation.
- Trains models on historical sensor data
- Identifies subtle patterns indicating wear
- Reduces unplanned downtime by up to 50%
Autonomous Decision-Making at the Edge
Advanced IoT Hubs now run lightweight AI models directly on the device. This enables instant responses—like shutting down a machine upon detecting overheating—without waiting for cloud instructions.
- Uses TensorFlow Lite or ONNX for edge inference
- Minimizes reliance on internet connectivity
- Enhances safety in critical systems
Explore AI at the edge with NVIDIA Jetson.
IoT Hub in Smart Cities and Urban Infrastructure
Smart cities rely on IoT Hubs to manage traffic, lighting, waste, and public safety. These hubs act as central nervous systems for urban intelligence.
Traffic Management and Public Transit Optimization
IoT Hubs collect data from traffic cameras, GPS, and sensors to optimize signal timing and bus routes. This reduces congestion and improves commuter experience.
- Adjusts traffic lights based on real-time flow
- Predicts delays and reroutes public transport
- Integrates with ride-sharing platforms
Smart Lighting and Energy Efficiency
Streetlights equipped with IoT sensors and connected to a central hub can dim when no one is around, saving energy and reducing light pollution.
- Reduces energy consumption by up to 60%
- Enables remote diagnostics and maintenance
- Supports environmental monitoring (noise, air quality)
Cities like Barcelona and Singapore have implemented large-scale IoT Hub networks for urban management.
Common Pitfalls When Deploying an IoT Hub
Even with the best technology, poor planning can lead to failure. Here are common mistakes and how to avoid them.
Underestimating Device Management Complexity
Managing thousands of devices requires robust tools for provisioning, monitoring, and updating. Many organizations fail to plan for this, leading to chaos.
- Use automated device onboarding
- Implement OTA update capabilities
- Monitor device health in real time
Ignoring Interoperability Standards
Without standardized protocols (like MQTT, CoAP, or Zigbee), devices from different vendors may not communicate, creating silos.
- Choose hubs that support open standards
- Avoid vendor lock-in
- Test integration before full deployment
What is an IoT Hub?
An IoT Hub is a centralized platform that connects, manages, and secures IoT devices. It enables bidirectional communication between devices and the cloud, supports device authentication, and facilitates data collection and command execution.
Which IoT Hub platform is best for enterprises?
Microsoft Azure IoT Hub and AWS IoT Core are top choices for enterprises due to their scalability, security, and integration with cloud services. The choice depends on existing infrastructure and specific use cases.
How secure are IoT Hubs?
Security varies by platform. Enterprise-grade IoT Hubs like Azure and AWS offer strong encryption, device authentication, and access controls. However, proper configuration and ongoing monitoring are essential to maintain security.
Can IoT Hubs work without internet?
Yes, many modern IoT Hubs support edge computing and local processing, allowing them to function during internet outages. They can store data locally and sync once connectivity is restored.
What industries benefit most from IoT Hubs?
Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, smart cities, and energy benefit significantly from IoT Hubs due to their need for real-time monitoring, automation, and predictive maintenance.
The IoT Hub is no longer optional—it’s essential. From smart homes to industrial automation and urban planning, it serves as the backbone of modern connectivity. As AI, 5G, and edge computing evolve, the role of the IoT Hub will only grow more powerful and pervasive. Choosing the right platform, securing your network, and planning for scalability are key to unlocking its full potential. Whether you’re a homeowner, engineer, or city planner, understanding the IoT Hub is the first step toward a smarter, more connected future.
Further Reading: